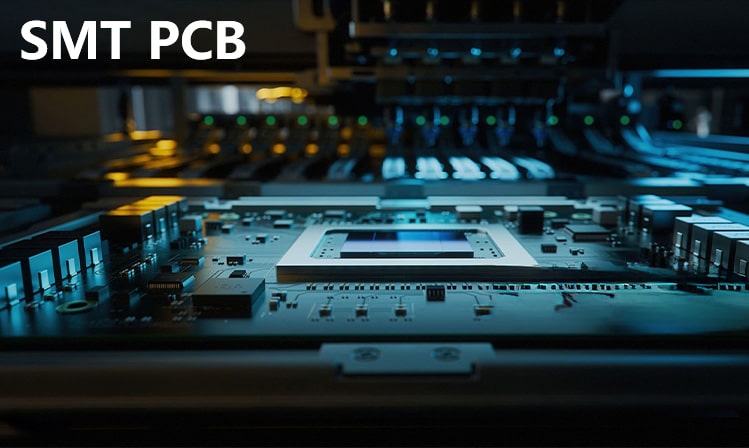
Surface mount technology (SMT) is a technology widely used in modern electronic manufacturing. It reduces space and improves production efficiency by directly mounting components on the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs). Let’s take a look at the soldering methods and soldering skills of SMT patch components.
SMT soldering method
1. Reflow soldering
Reflow soldering is the most common SMT soldering method, especially suitable for large-scale production. The process is as follows:
Printing solder paste: Print the solder paste onto the pads of the PCB through a template.
Patch components: Use a patch machine to place components on the solder paste.
Heating reflow: Transfer the PCB to the reflow oven, heat it through a temperature curve, melt the solder paste and solder it with the components.
Cooling and solidification: Finally, the solder joints are solidified by natural cooling or forced cooling.
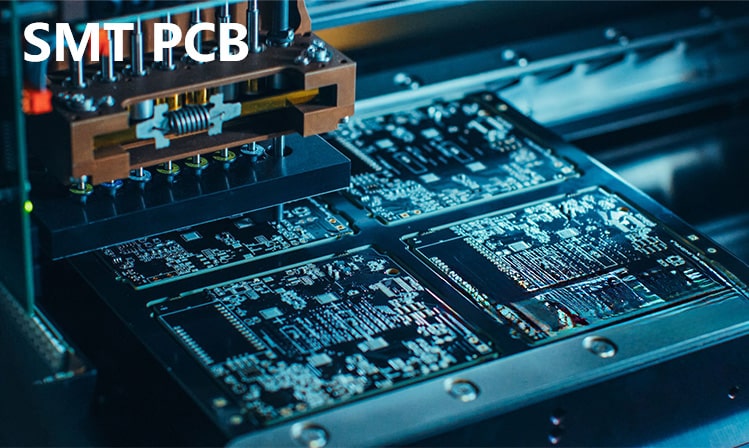
2. Wave soldering
Wave soldering is mainly used for double-sided PCBs or mixed technology boards:
PCB passes through the wave crest formed by molten solder to achieve soldering.
Suitable for larger components and through-hole components.
3. Manual soldering
Manual soldering is suitable for small batch production and repair work:
Use electric soldering iron to manually solder components.
Requires the operator to have a certain level of technical skills to ensure the quality of solder joints.
4. Selective soldering
Selective soldering is used in situations where precise soldering is required:
Use special equipment to selectively solder specific areas.
Suitable for complex circuit boards.
5. Laser soldering
Laser soldering is an advanced soldering technology:
Use a laser beam to heat the soldering material.
Precise and suitable for soldering of tiny components.
SMT soldering tips
1. Solder paste selection and application
Choose the appropriate solder paste according to the needs of components and PCBs.
The thickness of the solder paste is uniform to ensure the strength of the solder joints.
2. Temperature control
In reflow soldering, the control of the temperature curve is crucial.
Ensure that the temperature changes at different stages are smooth to prevent damage to components.
3. Equipment calibration
Regularly calibrate the placement machine and soldering equipment to ensure accuracy.
Check the operating status of the equipment to avoid failures.
4. Welding quality inspection
Use a microscope or X-ray equipment to detect the quality of solder joints.
Check whether the solder joints have cold soldering, false soldering or poor soldering.
5. Electrostatic protection
During the operation of electronic components, take good electrostatic protection.
Use anti-static wristbands and workbenches to prevent static electricity from damaging components.
There are various welding methods for SMT patch components. Choosing the right method and technique can improve production efficiency and product quality. Understanding the characteristics of different welding methods and selecting them according to specific needs and conditions is the key to success. Through scientific welding techniques and strict quality control, the reliability and performance of electronic products can be ensured.